Terrapreta Technology
About Terrapreta
With this more than 2,000-year-old method, agricultural waste is transformed into a soil enhancer that can store carbon, improve food security, boost soil biodiversity, and reduce deforestation.
The procedure yields a highly porous, fine-grained charcoal that aids in soils’ ability to hold onto moisture and nutrients.
Due to past soil management techniques and vegetation fires, Terrapreta can be found in soils all over the world. A greater understanding of Terrapreta’s special abilities as a soil enhancer has resulted from extensive research on biochar-rich dark earths in the Amazon (terra preta).
In regions with severely depleted soils, few organic resources, and insufficient amounts of water and chemical fertilizers, Terrapreta can be a crucial tool for boosting food security and agricultural diversity.
By enhancing soil retention of nutrients and agrochemicals for plant and crop utilization, Terrapreta also enhances water quality and quantity. More nutrients stay in the soil rather than contaminating groundwater by leaching.
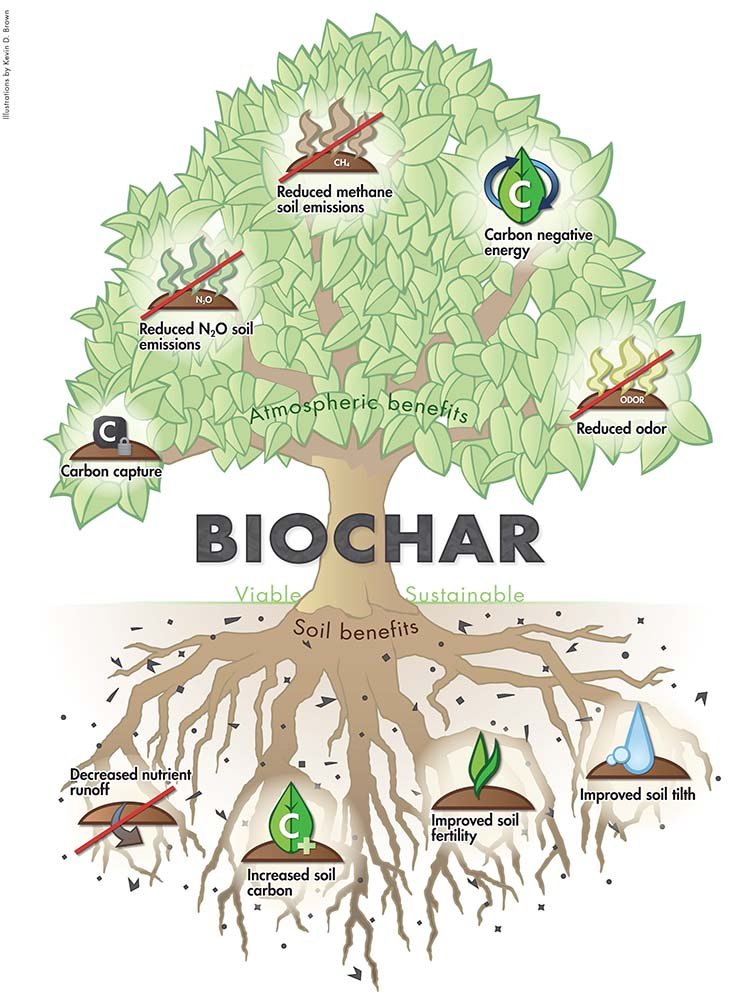
Terrapreta is a Powerfully Simple Tool to Combat Climate Change
The carbon in Terrapreta can keep carbon in soils for hundreds to thousands of years and is resistant to deterioration. Pyrolysis and gasification, which heat biomass without (or under reduced oxygen conditions), generate Terrapreta.
Sustainable Terrapreta production techniques can yield oil and gas byproducts that can be burned as fuel, generating clean, renewable energy in addition to improving soil. The system can turn “carbon negative” if the Terrapreta is buried beneath the surface to improve the soil.
Co-producing Terrapreta and bioenergy can help fight climate change by reducing the need for fossil fuels and storing carbon in secure soil carbon pools. Additionally, it might lessen nitrous oxide emissions.
This straightforward yet effective device can help us cut down on carbon emissions.
The real black gold
Pyrolysis technology turns existing biomass into valuable products of revolutionary Terrapreta, oil, and gas.
There are multiple productive and environmental uses for production. These include fertile soil for plants and the filtration of harmful chemicals.
The facility produces more energy than it consumes. Extra renewable energy can be used for heating, cooling, or desalination.
Indeed, fresh thinking helps us deliver even the most complex projects extraordinarily well for our clients, whether they’re architects or building owners. Advanced analysis enables us to confound convention and find solutions for seemingly impossible problems
Economics of Terrapreta
Terrapreta
286 tons
=
572, 000 €
Clean energy
1,428 MWh
=
171,360 €
CO2 removals (CO2 eq)
857 tons
=
52,962.6 €
It's Impact
Through the use of pyrolysis, our special, tested method transforms CO2, which is stored as short-cycle carbon in biomass, into Terrapreta, a mineralized form of long-cycle carbon.
There are many well-studied applications for Terrapreta that benefit the environment and society.
Around 3.5 kilograms of CO2 are permanently bound to the soil for every kilogram of terrapreta generated.
The energy from the biorefinery may produce 250,000 liters of fresh water per day by distilling seawater.
terrapreta permanently binds pollutants like mercury and phosphorus when used as a filter.